- A sound is also a form of energy like light energy, heat energy, kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Sound causes a type of sensation in our ears.
Production of sound
- The vibration of an object produces sound.
- The motion of objects or materials also causes vibration.
- Vibration is referred to as a to and fro motion. It is also called an oscillation.
Sound produced by humans
- In humans, the vibration of the larynx or voice box causes sound.
- It is located at the upper end of the windpipe. In the larynx, vocal cords are attached which has a narrow slit between them for the air to pass.
- Vocal cords have muscles which can lose or tight the muscles.
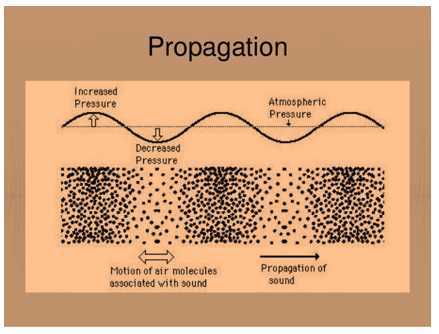
Propagation of sound
- Propagation of sound means the travelling of sound.
- The to and fro motion of various particles of the medium propagates the sound.
We hear sound with ears
- The sound is collected by the outer ear which is funnel-shaped. Later the wave of sound travels to the eardrum. The eardrum causes vibrations.
- The three bones of our middle ear that are stirrup, hammer and anvil amplify the vibrations. Then the sound is transmitted to the inner air.
- The brain gets the sound with the help of the inner air and we are able to hear the sound.
Amplitude of sound
- The maximum displacement related to the particle having a wave in a sound wave is called its amplitude.
- It is denoted by ‘A’. Unit is the SI meter.
Frequency of sound
- The frequency of sound is the number of oscillations and vibrations done by an object in a second.
- Frequency = Number of oscillations / Total time
Time period of sound
- Time period is referred to as the time taken by an object to complete one vibration or oscillation.
- It is denoted by ’T’. Second is the SI unit.
- Time period = time / numbers of vibration or oscillation.
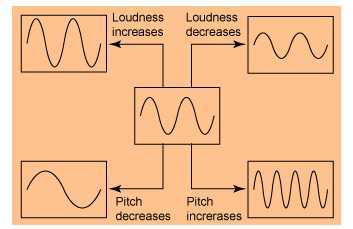
Loudness and pitch
- Loudness
- The measure of sound energy when it reaches the ear in a second is called the loudness of sound.
- Amplitude decides the softness or loudness of a sound.
- The unit decibel measures the loudness of sound.
- Pitch or shrillness
- When there is a sensation in an emitted sound of the frequency then it is called a pitch.
- A frequency of vibration decides the pitch of the sound.
Audible and Inaudible sounds
- Audible sounds have a frequency range of 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. He human beings can hear this sound.
- The inaudible sound is the sound below 20 Hz and above 20000 Hz. Some animals can hear this sound.
Noise and music
- Noise
- The sound which is not pleasant to hear is called as noise.
- Example is sound produced by the vehicles.
- Music
- The sound which is not pleasant to hear is called as noise.
- Example is the sound of musical instruments.
Noise pollution
- When a sound is produced that is loud, excessive, unbearable and unwanted to our ears and environment then it is called as noise pollution.
- Examples are High volume in televisions, the sound of vehicles, machines, loudspeakers, etc.
Problems due to noise pollution
- Lack of sleep
- Loss of hearing
- Hypertension
- Anxiety
- Temporary impairment
- Loss of hearing
Recap
- A sound is also a form of energy like light energy, heat energy, kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Sound causes a type of sensation in our ears.
- A vibration of the object produces sound.
- In humans, the vibration of the larynx or voice box causes sound.
- Propagation of sound means the travelling of sound.
- When a sound is produced that is loud, excessive, unbearable and unwanted to our ears and environment then it is called as noise pollution.
































Comments