Our environment is very beneficial to support life on planet earth. Without a good environment, it would have been very difficult to sustain life on this planet. So our environment plays a big role in helping us live and carries out our day to day activities.
There are two very important parts of our environment which help in sustaining life:
- Naturals Resources
- Water
Natural Resources
Natural resources are those gifts of nature which are present in nature without any action of mankind. Earth’s natural resources like light, air, water, plants, animals, soil, stone, minerals, and fossil fuels are very essential to sustain life on planet Earth.
Uses of Natural Resources in Daily Life
|
Natural Resource |
Products or Services |
|
Air |
Wind energy, tires |
|
Animals |
Foods (milk, cheese, steak, bacon) and clothing (wool sweaters, silk shirts, leather belts) |
|
Coal |
Electricity |
|
Minerals |
Coins, wire, steel, aluminium cans, jewellery |
|
Natural gas |
Electricity, heating |
|
Oil |
Electricity, fuel for cars and aeroplanes, plastic |
|
Plants |
Wood, paper, cotton clothing, fruits, vegetables |
|
Sunlight |
Solar power, photosynthesis |
|
Water |
Hydroelectric energy, drinking, cleaning |
Classification of Natural Resources
1.

EXAMPLES:
- Animals
- Fresh Air
- Water
- Land
- Plants

EXAMPLES:
- Coal
- Petroleum
- Minerals
- Metals
Apart from these two categories of natural resources, other categories are also defined to differentiate Natural Resources:

EXAMPLES:
- Plants
- Animals
- Trees

EXAMPLES:
- Air
- Water
- Land
- Soil
- Minerals
- Metals
Water
Along with air, Water is most essential for the existence of mankind. Water exists above the earth’s surface [in the form of clouds, fog, dew] and also below the earth surface.
Water is essential for the sustainability of human life. Water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2:1.
Occurrence of Water
Water can be found in different parts of the earth. They are:
- Oceans

They include the oceans, seas, rivers and lakes. They account for 3/4th of the water content on planet earth.
- Seawater has dissolved impurities.
- Dissolved impurities include unwanted minerals, salts and dissolved gases.
- River water has suspended impurities.
- Suspended impurities include clay, mud, gravel, dead plants and animals.
- Clouds and rain

The water from cloud and rain is derived from the water cycle itself.
The water which is available from the rain contains dissolved gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in the first showers.
- Glaciers and Snow
They account for 2% of the total water available on earth.
But most importantly they supply 98% of the total fresh water on earth.
So, Glaciers are essential for the sustainability of life on Earth.
More facts about the how important water is to sustain life on earth:
- The human body has a water content of 70%. And a loss of even 2% of this water can be harmful to life and leads to complete memory loss.
- The fruits and vegetables which are an important part of any diet has a water content of 75-80% which makes the water very essential for living beings on earth
Water Cycle
Water cycle can be defined as the circulation of water from the ‘earth surface’ to the atmosphere and then back to the earth again.
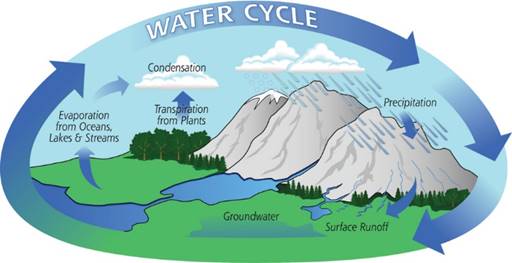
This water cycle is very important for life on earth and this maintains the essential balance required for the earth to be full of life.
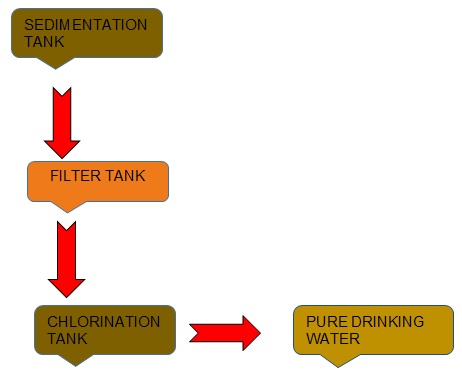
Purification of Impure Water
Purification of natural water for drinking purpose is generally done by passing the water through three tanks. They are:
Purification of sea water is done by the distillation process
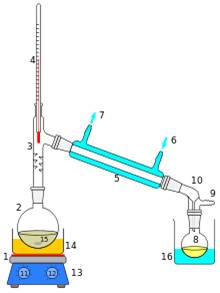
- Impure sea water is added to the flask of the apparatus.
- On heating the flask, the pure water evaporates and the vapours condense by the passage through the condenser.
- The condensed water is received on the smaller flask.
Properties of Water
- Colour: Water is a colourless liquid.
- Odour: Water is an odourless liquid.
- State: Water can exist in all three states: Ice (Solid), Water (Liquid), Water vapour (Gas).
- Boiling Point: 100 degree Celsius at 760mm pressure.
- Melting Point: 0 degree Celsius at 760mm pressure.
|
INCREASE IN PRESSURE (on water surface) |
Boiling point Melting point |
Increases Decreases
|
|
ADDITION OF SOLUTES (on water surface) |
Boiling point Melting point |
Increases Decreases
|
Anomalous expansion of water
- Al liquid contracts on cooling.
- Water also contracts on cooling until it reaches a temperature of 4 Degree Celsius.
- On Cooling below 4 Degree Celsius up to Melting Point, water expands instead of contracting.
- This behaviour of water is known as “anomalous”.
- The density of water is highest at 4 Degree Celsius.
Examples: Ice floats on the surface of the water and forms an insulating layer on the water allowing survival of fishes and aquatic animals below it.
This is one of the main applications of ‘anomalous expansion of water.
Conductivity of water:
- Thermal: Water is a bad conductor of heat.
- Electricity: Water is a bad conductor of electricity.
Tests for Water
Physical tests
The boiling and freezing points of water are taken as the physical tests.
- Water is taken in a test tube
- It is heated or put on crushed ice.
- The water is heated until it forms steam or cooled until it forms ice.
- The constant Temperature is noted.
- Thus, we become sure that it is water by seeing the temperatures
Chemical Tests
Water turns Anhydrous Copper Sulphate Blue is the chemical test.
Solubility
- The solubility of most solids in water increase with an increase in temperature.
- Liquids which are soluble in water is called miscible liquid.
- The solubility of gases is inversely proportional to the temperature and directly proportional to the pressure of Water.
Recap
- Water is essential for the sustainability of human life. Water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2:1.
- Water is found naturally in oceans, clouds and glaciers.
- Water cycle can be defined as the circulation of water from the ‘earth surface’ to the atmosphere and then back to the earth again.
- Purification of sea water is done by the distillation process.
Ice floats on the surface of the water and forms an insulating layer on the water allowing survival of fishes and aquatic animals below it.
- The boiling and freezing points of water are taken as the physical tests.
- Water turns Anhydrous Copper Sulphate Blue is the chemical test.
- Water is a bad conductor of heat and electricity.
- Natural resources are those gifts of nature which are present in nature without any action of mankind.
- Renewal Resources: They can be regained by the efforts of people after they get exhausted.
- Examples are plants, animals.
- Non-Renewal Resources: They are present in small quantity and never be regained either from earth or by human beings after getting exhausted
- Examples are coal and petroleum.
- Biotic resources: These resources have life and help us to sustain life on earth.
- Examples are plants and animals.
- Abiotic resources: These resources are non-living things which are helpful for our lives.
- Examples are air, water.


























Comments