Every element which has its existence on planet earth are characterized by metals and non-metals depending on their properties. One of the properties which exist between them. Metals when in their pure state have a shining surface due to a metallic lustre.
Difference between Metals and Non-Metals
(i) All metals except mercury exist as solids at room temperature.
Metals have high melting points but gallium and caesium have very low melting points.
These two metals will melt if you keep them on your palm.
(ii) Iodine is a non-metal but it is lustrous.
(iii) Carbon is a non-metal that can exist in different forms. Each form is called an allotrope. Diamond, an allotrope of carbon, is the hardest natural substance known and has a very high melting and boiling point. Graphite, another allotrope of carbon, is a conductor of electricity.
(iv) Alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potassium) are so soft that they can be cut with a knife. They have low densities and low melting points.
What Happens When a Metal is Burnt in Air?
Almost all metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides.
Metal + Oxygen = Metal oxide

What Happens When a Metal Reacts With Water?

What Happens When a Metal React With Acid?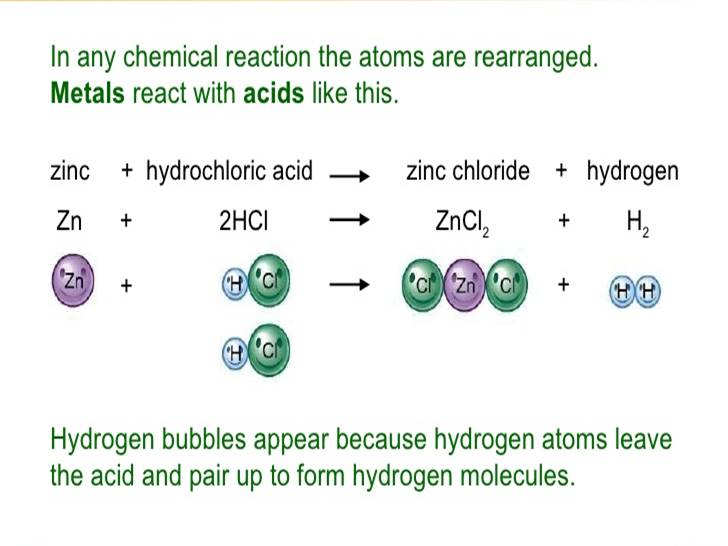
The Reactivity Series

Properties of Ionic Compounds
(i) Physical nature: Ionic compounds are solids and are somewhat hard because of the strong force of attraction between the positive and negative ions. These compounds are generally brittle and break into pieces when pressure is applied.
(ii) Melting and Boiling points: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points (see Table 3.4). This is because a considerable amount of energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction.
(iii) Solubility: Electrovalent compounds are generally soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene, petrol, etc.
(iv)Conduction of Electricity: The conduction of electricity through a solution involves the movement of charged particles. A solution of an ionic compound in water contains ions, which move to the opposite electrodes when electricity is passed through the solution. Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because the movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure. But ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state. This is possible in the molten state since the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome due to the heat. Thus, the ions move freely and conduct electricity.
Recap
- Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals.
- Metals are lustrous, malleable, and ductile and are good conductors of heat and electricity. They are solids at room temperature, except mercury which is a liquid.
- Metals can form positive ions by losing electrons to non-metals.
- Metals combine with oxygen to form basic oxides. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide show the properties of both basic as well as acidic oxides. These oxides are known as amphoteric oxides.
- Different metals have different reactivities with water and dilute acids.
- A list of common metals arranged in order of their decreasing reactivity is known as an activity series.
- Metals above hydrogen in the Activity series can displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
- A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
- Metals occur in nature as free elements or in the form of their compounds.
- The extraction of metals from their ores and then refining them for use is known as metallurgy.
- An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.
- The surface of some metals, such as iron, is corroded when they are exposed to moist air for a long period of time. This phenomenon is known as corrosion.
- Non-metals have properties opposite to that of metals. They are neither malleable nor ductile. They are bad conductors of heat and electricity, except for graphite, which conducts electricity.



























Comments