One of our basic necessities is cloth. Clothes make us civilized and smart and also protects from cold, heat, insects, dust, rain, etc. Clothes are made up of cloth which is also known as fabric.
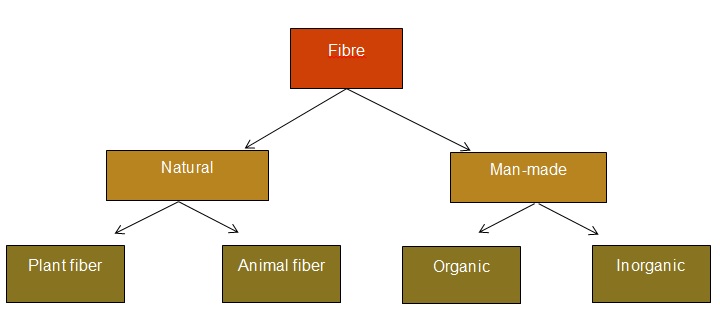
Fibers are of two types-
- Natural Fiber
- Manmade Fiber
Natural fibers- We get natural fibers from plants and animals such as cotton, jute, silk, wool, etc.
Manmade fibers- Manmade fibers are the ones which are synthesized in the laboratory such as terry-cotton, terylene, acrylic etc.
Plant fiber- When the fiber is obtained from plants than it is called as plant fiber. For example- cotton, flex, jute, etc.
Animal fiber- When the fiber is obtained from animals than it is called an animal fiber. For example - silk and wool.
Organic fiber - When the fiber is made by transforming the natural polymers and synthetic polymers than it is known as organic fiber. For example - regenerated cellulose, polyesters.
Inorganic fibers - The fibers which are inorganic in nature are carbon, ceramic, etc.
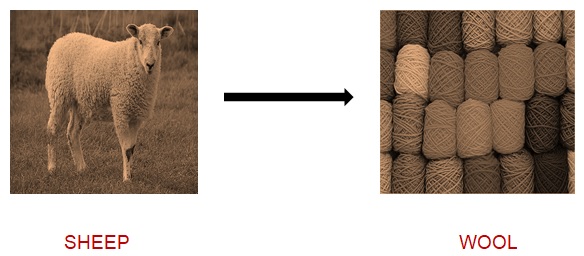
Wool

There are various animals that have a very thick layer of hair on their body. These type of animals live in cold weather. This layer of hair keeps the animal warm and prevents them from coldness to enter the surroundings. For example- yak, sheep, goat, camel, etc.
Wool and fleece-bearing animals- These animals have two types of hair – coarse hair and fine –soft under hair. Fine soft hair is also called as fleece. Fiber for wool is found in the fleece and so such animals are known as wool bearing animals.
Process to obtain wool from sheep-
- Shearing – The hair of the sheep along with the layer of skin is shaved off using a machine. Earlier blades were used for this process. Shearing is mostly done in summers so that new hair gets grown up by winter to protect sheep from cold.
- Sourcing – After shearing fleece is washed so as to avoid any dirt and grease. This process is called sourcing.
- Sorting – According to the texture fleece are sorted. This process is called sorting.
- Picking – After sorting, fluffy fibers which are called as burr are taken out from hair. Wool is obtained from burr.
- Dying – Burr is dyed in desired colours after sorting and picking.
- Spinning – At last the fibers are straightened, combed and then rolled into yarns.
Silk
Another important animal fiber is silk. To obtain silk silkworm is reared. Different types of silk are produced by different silkworms. For example; mooga silk, tassar silk, etc. are formed from various types of the silk moth. The most common silk moth is Mulberry silk.
Rearing of silkworm – Rearing of the silkworm is called as Sericulture. Silkworms are traced on mulberry leaves.

Lifecycle of silkworm
Female silk moth lays eggs and after about 14 days these eggs are hatched into larva. Then the larva is grown into a pupa and itself weaves a net. Then the liquid protein is produced from the salivary glands and moves its head in the shape of ‘8’. They live in the cocoon for some time and after coming out silk moth is formed from the cocoon.
Obtaining of silk from the cocoon –
Firstly, cocoons are boiled to separate the silk fiber using machines. Silk thread is unwound from cocoons with the help of a machine. The silk thread than obtained is woven into various types of cloth.
Recap
- A cloth is our basic need which protects us from rain, wind, insects, etc.
- Fibers are of two types natural and manmade. Natural fiber includes jute, wool, silk, cotton, etc. and manmade fiber includes terry-cotton, terylene, acrylic etc.
- Further Natural fiber is divided into two parts- plant fiber and animal fiber.
- Wool is obtained from sheep in the following process-
-Shearing
-Sourcing
-Sorting
-Picking
-Dying
-Spinning
- Silk is formed with the help of silkworm which has a complete lifecycle.






























Comments