All matters in the world are made up of elements. And the basic building blocks of elements and compounds are made up of atoms and molecules. The invention of atoms and molecules exist in elements is the first advancement in the world of research regarding nanoparticles.
Laws of Chemical Combination
1. Law of conservation of mass
Law of conservation of mass states that “mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction".
2. Law of constant proportion
According to the law of constant, “In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass".
Dalton’s Postulate Regarding Atoms

- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
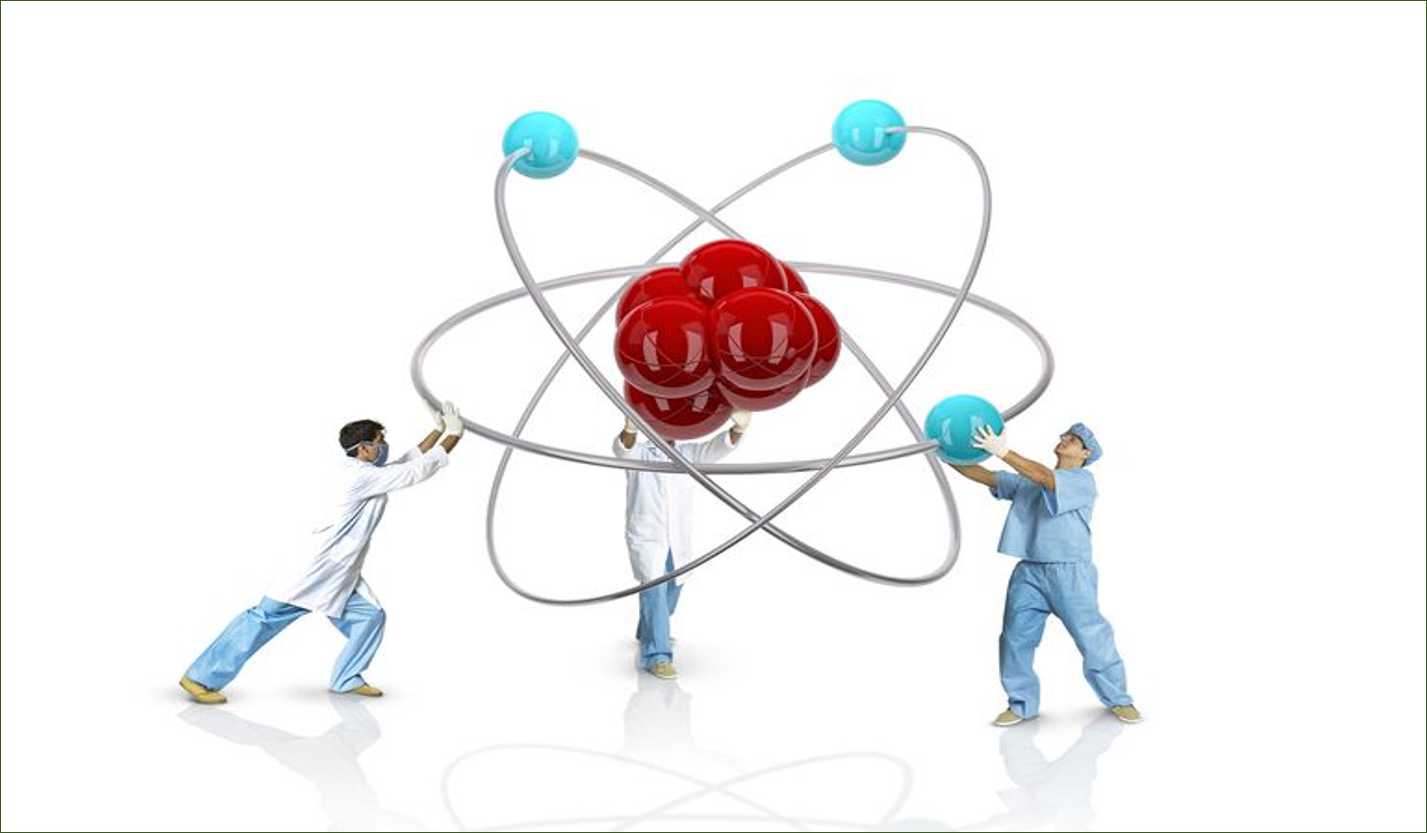
Atoms
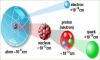
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of matter that has the properties of a chemical element. It has two parts. One of them is the nucleus which has the main mass of the atom and comprises of neutrons and protons. And around the nucleus, there are stationary orbits on which the electrons revolve.
Symbols for Elements
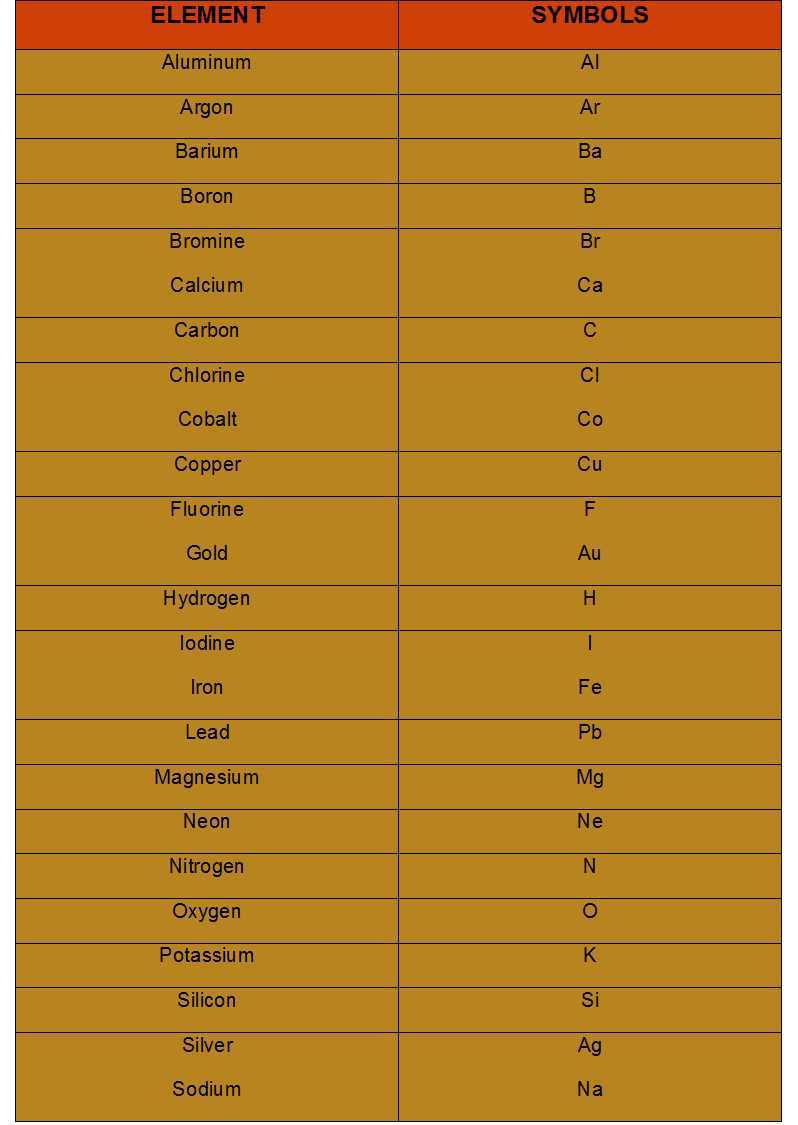
Dalton was the first scientist who was known to use the symbols for elements in a very specific sense. When he used a symbol for any element he would even define a definite quantity of that element which is one atom of that element.
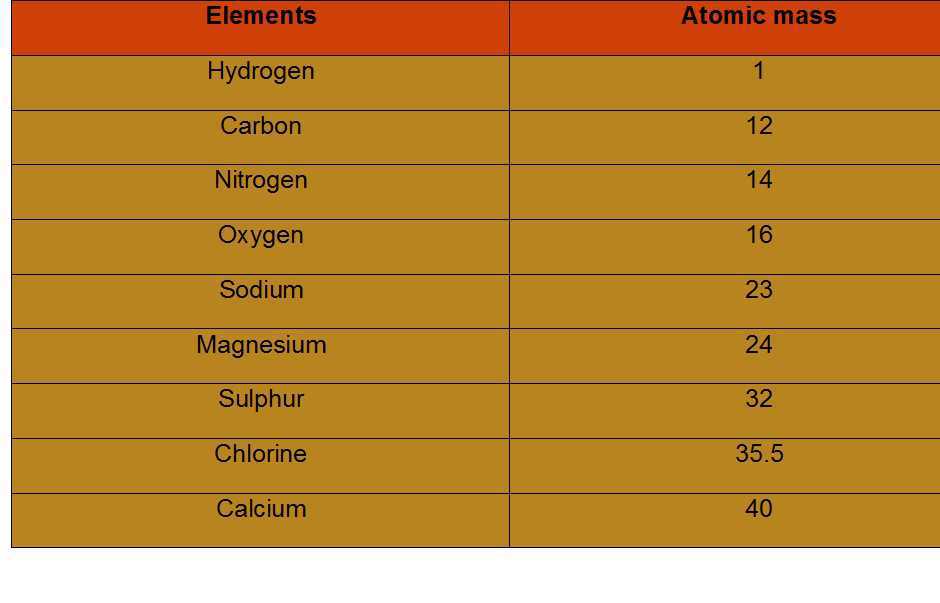
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass is the characteristic mass of each atom in each element. One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12. Carbon-12 isotope was chosen as the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
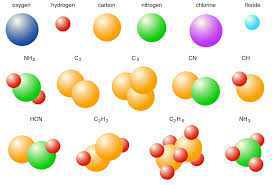
 Molecules
Molecules
A molecule is, in general, a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together that is, tightly held together by attractive forces. A molecule can be defined as the smallest particle of an element or a compound that is capable of an independent existence and shows all the properties of that Substance. Atoms of the same element or of different elements can join together to form molecules.
Rules for Writing Formulas of Compounds
- The valencies or charges on the ion must be balanced.
- When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the name or symbol of the metal is written.
- In compounds formed with polyatomic ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio. In case, the number of a polyatomic ion is one, the bracket is not required.
Examples:
- Formula of hydrogen chloride
Formula: HCl
- Formula for aluminum oxide:
Formula: Al2O3
- Formula of sodium nitrate:
Formula: NaNO3
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is, therefore, the relative mass of a molecule expressed in atomic mass units (u).
Recap
- During a chemical reaction, the sum of the masses of the reactants and products remains unchanged. This is known as the Law of Conservation of Mass.
- In a pure chemical compound, elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass. This is known as the Law of Definite Proportions.
- An atom is the smallest particle of the element that cannot usually exist independently and retain all its chemical properties.
- A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound capable of independent existence under ordinary conditions. It shows all the properties of the substance.
- A chemical formula of a compound shows its constituent elements and the number of atoms of each combining element.
- Clusters of atoms that act as an ion are called polyatomic ions. They carry a fixed charge on them.
- The chemical formula of a molecular compound is determined by the valency of each element.
- In ionic compounds, the charge on each ion is used to determine the chemical formula of the compound.
- Scientists use the relative atomic mass scale to compare the masses of different atoms of elements. Atoms of carbon-12 isotopes are assigned a relative atomic mass of 12 and the relative masses of all other atoms are obtained by comparison with the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
- The Avogadro constant 6.022 × 1023 is defined as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12.
- The mole is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles (atoms/ ions/ molecules/ formula units etc.) as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12.
- Mass of 1 mole of a substance is called its molar mass.


























Comments