- Cells are the basic structural units in the living organisms.
- Cell is the functional and structural unit of life.
- A cell has a size of 1 to 100 micrometer.
- The division of the preexisting cells produces the other cells.
- The physiological and chemical functions that happen inside the cells are growth, repairing, immunity, digestion and communication.
Types of Cell
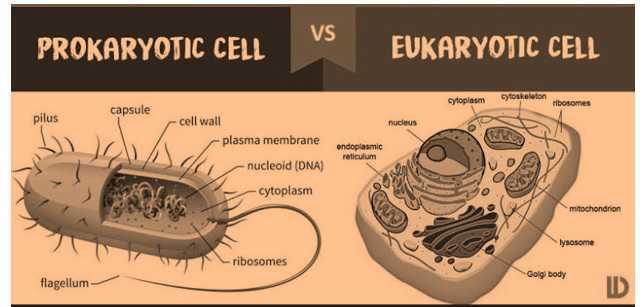
- Prokaryotic cells
- These cells without nuclear membrane have nuclear material.
- When the organisms have these kinds of cells, then they are called as prokaryotes.
- Examples are blue green algae and bacteria.
- Eukaryotic cells
- These cells have a nuclear membrane and well organized nucleus.
- All the organisms other than the blue green algae and bacteria are called as Eukaryotic cells.
Shape of cells
- Cells are generally spherical, rounding or elongated. Some cells are tend to be long and are pointed at the ends.
- Membrane is enclosed with the components of the cell.
Size of cells
- A cell can be large as in centimeters or as small as in millionth.
- Cells are usually microscopic in the size.
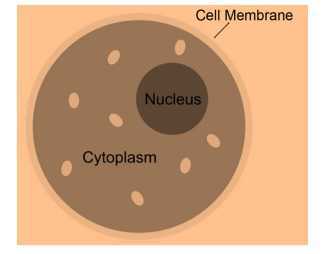
Parts of the cell
- Cell Membrane
- Inside the cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm are present, it is also known as plasma membrane.
- It is thin, a living part, elastic and delicate.
- Cell gets the shape from cell membrane.
- Cytoplasm
- It has a jelly-like structure which is present between the nucleus and the cell membrane.
- Other components of cell like Golgi bodies, ribosomes, mitochondria, etc. are present in the cytoplasm.
- Nucleus
- It consists of a nucleus which has a thread like structure known as chromosomes.
- It is a spherical organelle which is present in the center of the cell.
- Genes are stored in the nucleus. Cell cannot survive without nucleus.
Recap
- Cells are the basic structural units in the living organisms.
- Cell is the functional and structural unit of life.
- A cell has a size of 1 to 100 micrometer.
- The division of the preexisting cells produces the other cells.
- Cells are generally spherical, rounding or elongated. Some cells are tend to be long and are pointed at the ends.
- A cell can be large as in centimeters or as small as in millionth.
- Cells are usually microscopic in the size.
































Comments